HPE Ezmeral CP (optional)
note
This document is a work-in-progress.
In this section we apply the concepts learned in the previous lesson and we deploy our custom application to the HPE Ezmeral Container Platform.
Previously we deployed a docker registry in our lab environment and pushed the docker image for our KD application there. For deploying our KD application to Ezmeral Container Platform we will enable Harbor as the registry.
Create a Kubernetes Cluster
Using the HPE Ezmeral Container Platform user interface create a Kubernetes cluster.
Create a Tenant
Using the HPE Ezmeral Container Platform user interface create a tenant for your Kubernetes cluster.
Ensure Harbor addon is enabled
info
This step uses the hpecp CLI. You can install it with:
After installing, configure with:
If the above command fails, ensure your PATH contains the output from the following command:
You can test the CLI is set up correctly with the following command which connects to the HPE Ezmeral cluster and retrieves it's build version.
First we want to list the K8S clusters:
This will return something like:
We can then get the details for the cluster we are interested in - in this particular case /api/v2/k8scluster/1:
This will returns something like the following:
You can see that harbor addon is enabled. If the harbor is not enabled, you can enable it like this:
Retrieve the Harbor url
In the output from hpecp k8scluster get /api/v2/k8scluster/1, above you can see that
my harbor endpoint is:
https://ip-10-1-0-108.eu-west-3.compute.internal:10004
Login to Harbor
Open a browser to the harbor endpoint and login with:
- Username
admin - Password
Harbor12345
Download the registry certificate
Click the Projects link:

Next click on the link that corresponds to your HPE Container Platform tenant (in my case k8s_tenant_1)
and then select the Repositories tab.
Click on REGISTRY CERTIFICATE to download it:

Copy certificate to HPE CP nodes
In this step, we will copy the ca.crt downloaded from the previous step to the k8s hosts.
Retrieve the IP addresses of your k8s worker hosts.
Retrieve K8S host IP addresses
You can use the HPE Ezmeral Container Platform UI or the CLI to find the IP addresses.
The CLI can be used like this:
For CENTOS/RHEL 7x:
- Copy ca.crt to each worker and master in the folder:
/etc/pki/ca-trust/source/anchors/ - Run
update-ca-truston each host after adding the ca.crt
Create a basic config package
In this section we modify the centos application to log the action inside the container.
Create a directory on the master: e.g. /home/centos/deploy/example_catalog/mycentos. Inside that directory,
create another directory appconfig and inside that folder, create a new file named startscript with the contents:
Open a terminal and change into the folder /home/centos/deploy/example_catalog/mycentos.
Create a tar file with the appconfig:
Update the Dockerfile so that it now contains:
Retrieve the tag and push commands
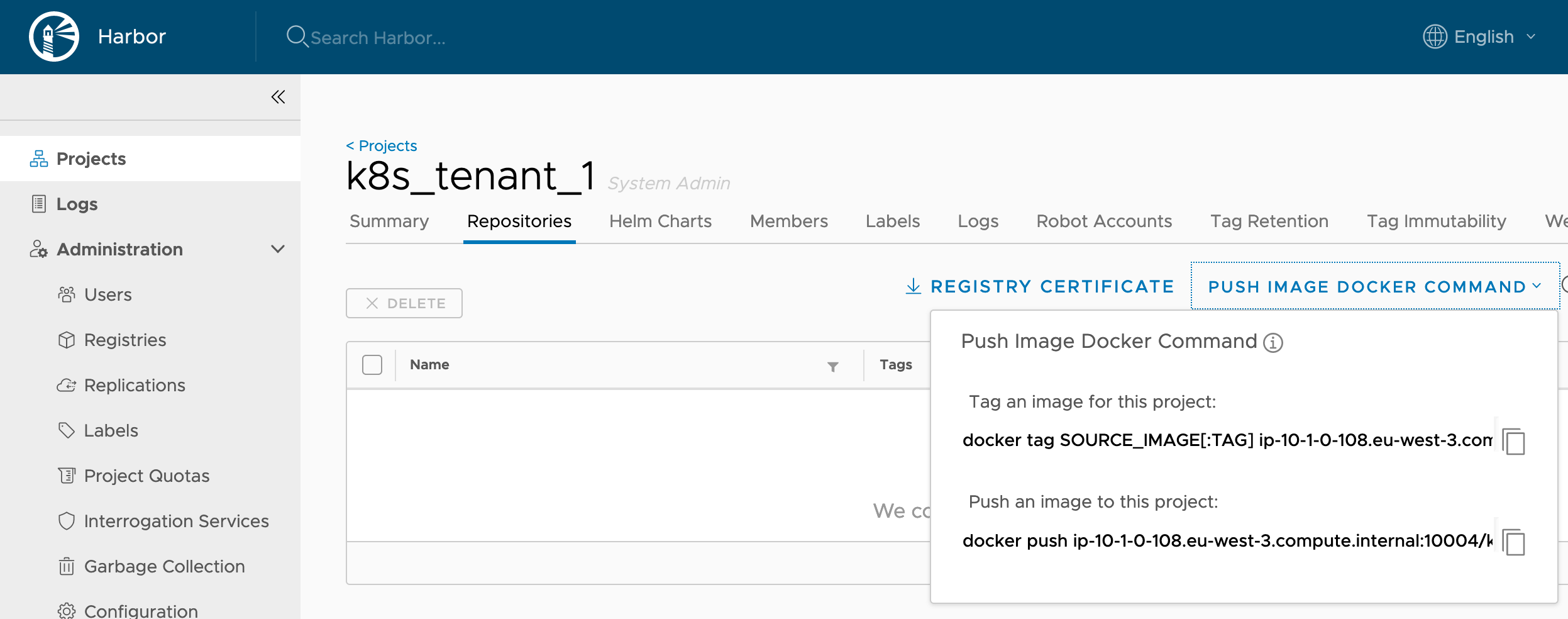
E.g.
docker tag SOURCE_IMAGE[:TAG] ip-10-1-0-108.eu-west-3.compute.internal:10004/k8s_tenant_1/IMAGE[:TAG]docker push ip-10-1-0-108.eu-west-3.compute.internal:10004/k8s_tenant_1/IMAGE[:TAG]
You will use these commands below.
Build and Push image
In the terminal, change to the mycentos folder and build your custom image and push it to the local registry:
Next we push the image to our local registry:
Copy the KD app image definition
Create a file /home/centos/deploy/example_catalog/cr-app-centos7-custom.json with the contents:
Rename:
to
Update the KD app image
Ensure defaultConfigPackage in the file /home/centos/deploy/example_catalog/cr-app-centos7-custom.json is set to:
and defaultImageRepoTag is:
Replace {{YOUR_REPO}} with your repo url. Mine was ip-10-1-0-108.eu-west-3.compute.internal:10004/k8s_tenant_1.
Deploy the KD app image
Deploy the new Centos KD application with your changes:
Check the deployment was successful:
You can see my image has only just been deployed:
Deploy the KD Cluster
First create a file /home/centos/deploy/example_clusters/cr-cluster-centos7-custom.yaml with the contents:
Next we can deploy the KD Cluster:
You may need to run the above command several times until the Cluster is stable:
You should see a new pod:
Wait a few seconds and try ls /opt again - keep trying until you see a guestconfig folder:
If we cat configure.stdout we should see the output from our startscript: