Creating a NiFi Application
In this session we will create a basic Apache NiFi KD Application and deploy it to HPE Container Platform.
The application is intentionally kept simple to simplify learning. Exercises will be suggested at the end of this lesson to add more features.
We do NOT need the kubedirector-lab in this session.
Functionality Walkthrough
After following this lesson you will have a NiFi tile in your list of Applications:

If you select the Service Endpoints menu, you should see a http endpoint:
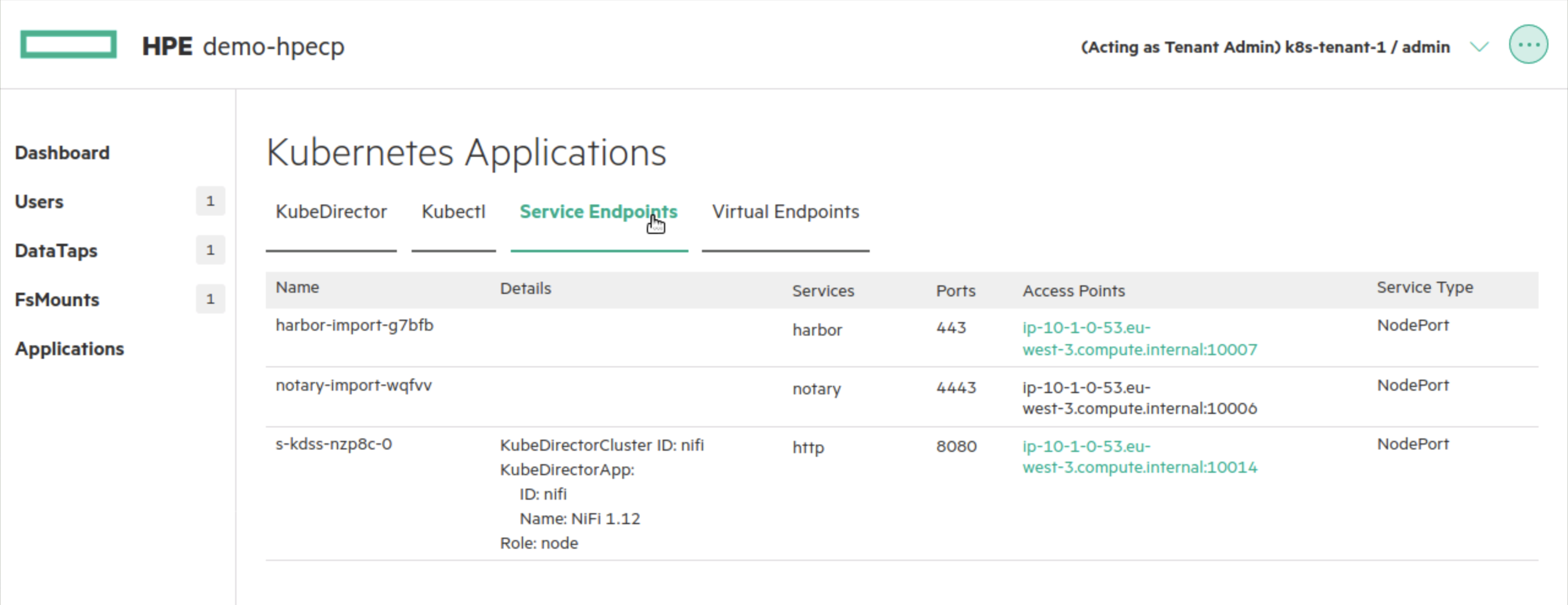
If you select the link for the http endpoint, you should see a NiFi page:

info
If you see a HTTP 503 error wait a few minutes for the NiFi service to start and then try again.
You should then see the NiFi canvas:
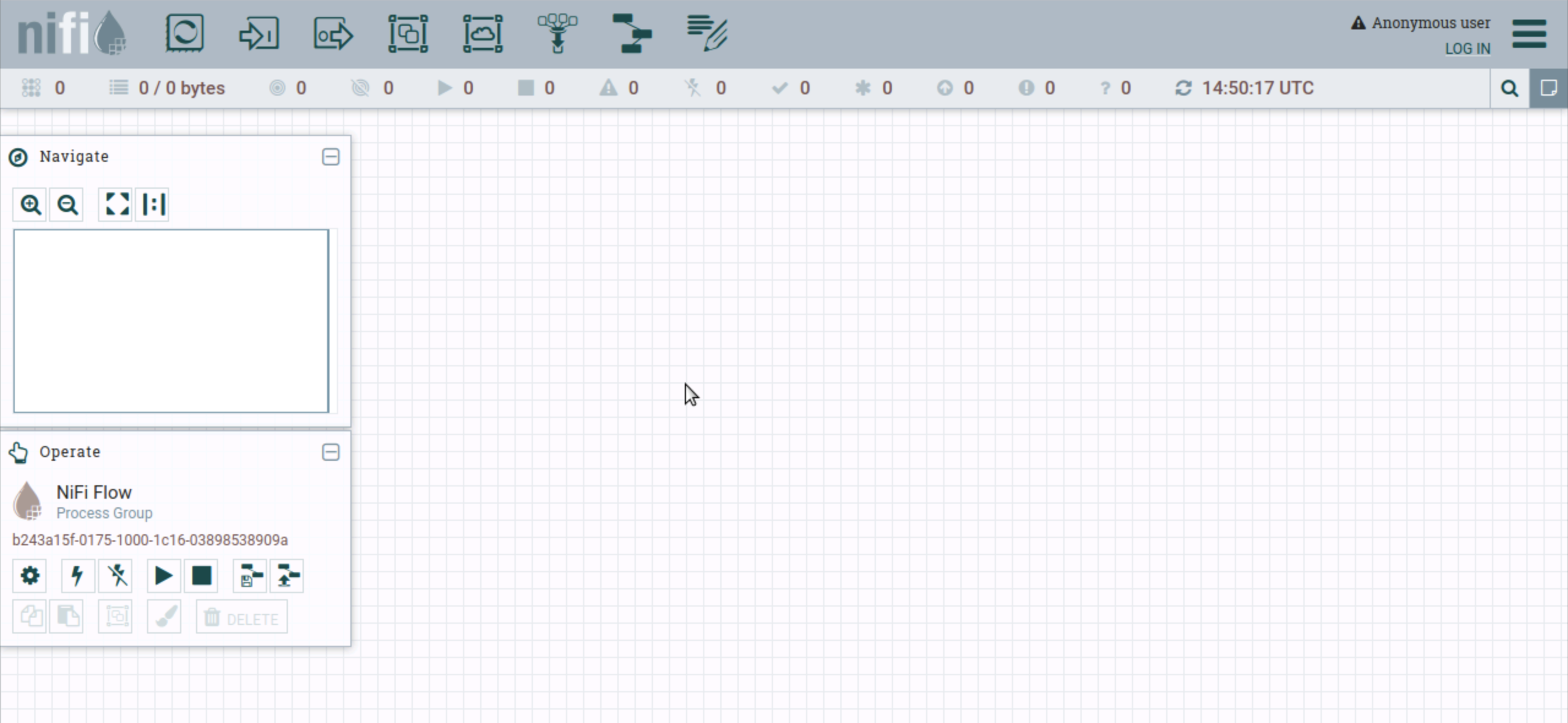
Installing the NiFi App and provision a cluster
The easiest way to deploy the application is to use the Terminal in a HPE Container Platform Kubernetes Tenant:
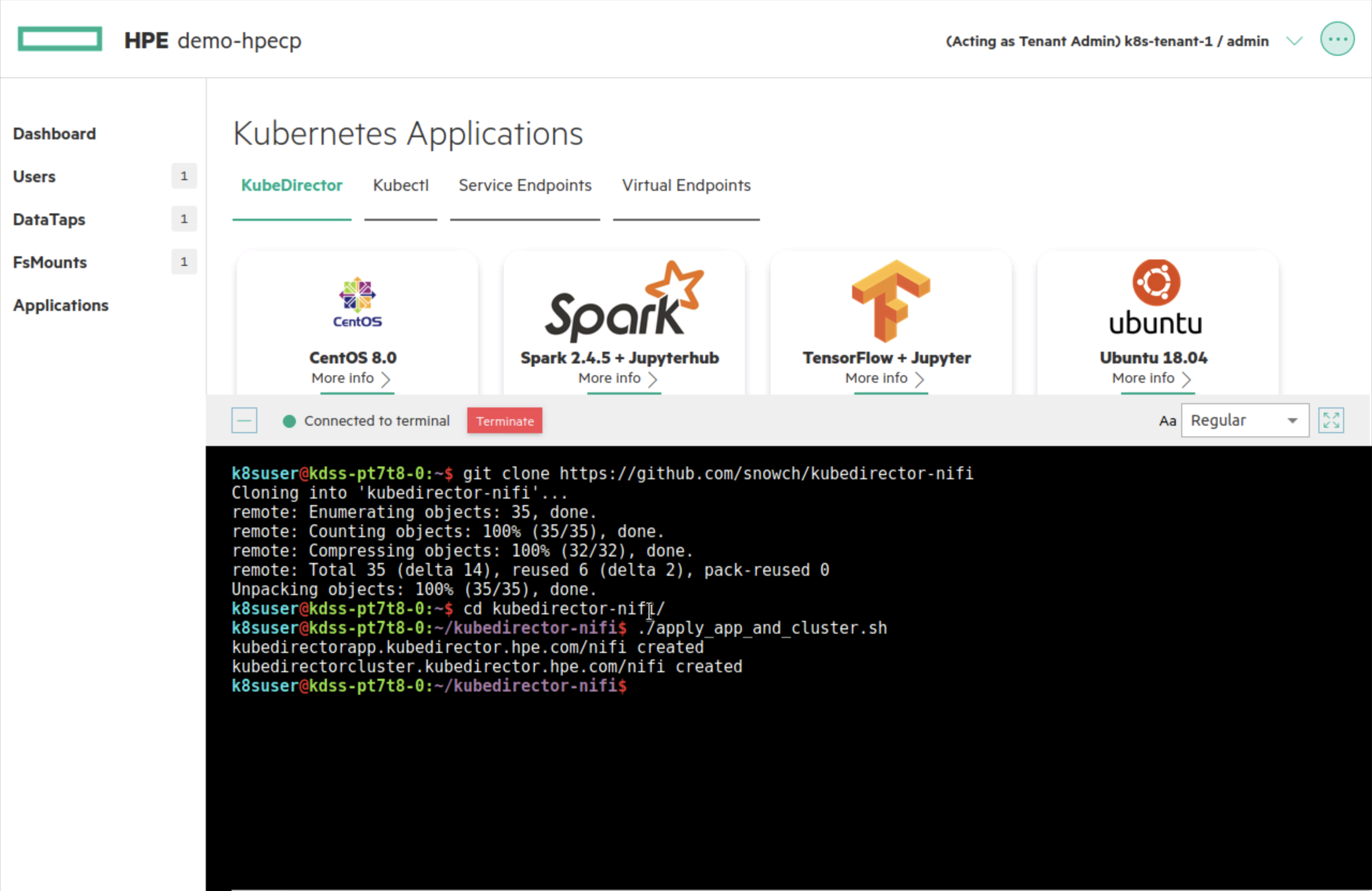
The steps are repeated below:
Application Walkthrough
The application currently resides in kubedirector-nifi.
Inside the kubedirector-nifi git repository there are some files and some submodules (other git repositories):
The cr-app-nifi.json file contains the application definition. The interesting parts of the application are:
If was assumed that the docker image would not need to be changed very often when developing the application so it was put in its own git repository kubedirector-nifi-docker-image. The image has been pushed to docker hub using the tag: snowch/kubedirector-nifi:latest.
It was assumed that the config package could change quite a lot so this was also put in its own git repository kubedirector-nifi-appconfig. Every time the app config is modified a git release artifact is created which can be accessed over http.
This approach allows anyone extending this application to easily change the appconfig and make it available over http.
Exercises
- Follow the instructions here to support multiple nodes on the NiFi cluster. You will need to use the configcli and respond to the lifecycle events.
- Add a new role which has a haproxy or nginx as a load balancer that uses the
configclito retrieve all of the nodes http endpoints and adds the endpoints to the routing configuration when a node is added or deleted.